Nov 2020
17
National Minimum Wage to increase by 10c per hour
The National Minimum Wage is going to increase from €10.10 per hour to the new rate of €10.20 per hour and this comes into effect from 1st January 2021. This increase will affect around 122,000 employees, increasing their national minimum wage by 0.9%. An employee working 40 hours a week will see their gross wages increase by €4.00 per week.
Minister for Social Protection, Heather Humphreys advised the minimum wage has increased by approximately 18% from the rate of €8.65 per hour in 2016 to the new rate of €10.20 per hour for 2021. She also assured that the PRSI thresholds would be changed in order to reflect the increase in the Minimum Wage.
Heather Humphreys stated that:
“I also want to ensure that the increase in the minimum wage does not result in employers having to pay a higher level of PRSI charge solely due to this increase. I will make regulations that will increase the employer PRSI threshold from €395 currently to €398 from 1st January 2021.”
The General Secretary of the retail union Mandate, Gerry Light, and the General Secretary of the Irish Congress of Trade Unions, Patricia King, resigned from their positions in the Low Pay Commission as they felt the 10c increase in the National Minimum Wage was not sufficient in meeting the needs of the minimum wage employees.
Make sure you keep up-to-date with the latest legislation changes. Subscribe to our newsletter today.
Sep 2018
12
National Minimum Wage - Increasing Jan 19
Currently, the national minimum wage is €9.55 per hour, which increased on 1st January 2018. The Low Pay Commission has recommended that the national minimum wage be increased by 25 cent to €9.80 per hour. The Government has accepted this recommendation and this increase is due to be introduced in January 2019.
This is the fifth increase of the national minimum wage since 2011. This increase could benefit up to 120,000 employees, increasing their hourly rate by 2.6%. An employee working 40 hours per week will see their gross pay increase by €10.00.
The new minimum hourly rates will be:
- Experienced adult worker – €9.80
- Under age 18 – €6.86
- In the first year after the date of first employment over age 18 - €7.84
- In the second year after the date of first employment over age 18 - €8.82
- In a course of training or study over age 18, undertaken in normal working hours-1st one third period: €7.35; 2nd one third period: €7.84; 3rd one third period: €8.82
The Taoiseach, Leo Varadkar said “this increase will put us in the top five in the world for our national minimum wage in cash terms and purchasing power.”
Related Articles:
- GDPR & Payroll Processing: Do I need consent from my client’s employees?
- PAYE Modernisation - List of Employees
- PAYE Modernisation: What you need to know
- What happens if I don’t comply with the GDPR ?
Are you missing out on our newsletter? We will not be able to email you without you subscribing to our mailing list. You will be able to unsubscribe at any time. Don’t miss out - subscribe today!
Jan 2018
2
Increase to Minimum Wage from January 2018
The National Minimum Wage for an experienced adult worker is increasing to €9.55 per hour from January 1st 2018. This is the third year in a row that the NMW has been increased but this is by far the largest with an increase of .30c
The National Minimum Wage Act, 2000 provides for a minimum hourly rate of pay for all workers.
All workers, including full time, part time, casual and temporary will be deemed to be covered by the act with only 2 exceptions; close relatives of the employer and certain industry specific apprentices.
Workers can be broken down into 5 different categories; experienced adult workers in employment more than 2 years and over the age of 18, a worker under the age of 18, workers in their first and second year of employment who are over the age of 18 and trainees’ who are undergoing a course that satisfies certain conditions set out in the Act.
The new minimum hourly rates are:
- Experienced adult worker – €9.55
- Under age 18 – €6.69
- In the first year after the date of first employment over age 18 - €7.64 per hour
- In the second year after the date of first employment over age 18 - €8.60
- In a course of training or study over age 18, undertaken in normal working hours-1st one third period: €7.17 per hour; 2nd one third period: €7.64; 3rd one third period: €8.60 per hour.
Breaches of the act are deemed to be criminal offences and are punishable with hefty fines and even imprisonment.
Thesaurus Payroll Manager | BrightPay Payroll Software
Related Articles:
Sep 2017
22
Public Holiday Pay Entitlement
There can often be some confusion surrounding an employee's entitlement to pay for a public holiday particularly where the employee may be part-time or the public holiday falls on a day that the employee does not normally work.
It is also worth noting that not every bank holiday is a public holiday though in most cases they coincide. Good Friday is a bank holiday but it is not a public holiday. The following dates are the official public holidays in Ireland.
- New Year's Day (1 January)
- St. Patrick's Day (17 March)
- Easter Monday
- First Monday in May, June, August
- Last Monday in October
- Christmas Day (25 December)
- St. Stephen's Day (26 December)
Employees who qualify for public holiday benefit will be entitled to one of the following:
- A paid day off on the public holiday
- An additional day of annual leave
- An additional day's pay
- A paid day off within a month of the public holiday
So, who is entitled to a payment?
- Part-time employees qualify for public holiday entitlement if they have worked at least 40 hours in the 5 weeks ending the day before the public holiday.
- Full time employees are not required to have worked up a minimum number of hours.
How to calculate the amount to be paid?
If the public holiday falls on a day which the employee would normally work:
- Full-time employees are entitled to one of the above four options at the employer’s discretion.
- Part-time employees have the same entitlement, so where the employee’s pay is a fixed amount the normal daily rate can be used. If the pay varies, the daily rate should be calculated over the 13 weeks immediately before the public holiday in question.
If the public holiday falls on a day which the employee does not normally work:
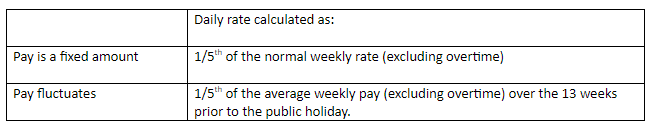
Further information can be found at Organisation of Working Time Act 1997.
Jul 2017
6
Living Wage increased by 20 cent
The 2017 Living Wage has been set at €11.70 per hour, up from €11.50 last year. The new figure represents an increase of 20 cent per hour on the previous rate. The recommended living wage rate is now nearly a third higher than the legally required minimum wage, which is set at €9.25 an hour.
The 20 cent increase in the Living Wage was arrived at upon consideration of a number of changes in the cost of living and the taxation regime in the last year. The Living Wage for the Republic of Ireland was established in 2014, and is updated in July of each year. It is part of a growing international trend to establish an evidence-based hourly income that a full-time worker needs so that they can experience a socially acceptable minimum standard of living.
Mar 2017
31
Important Information for Employers - Changes to Civil Service Travel Rates
Where employees use their own private cars or motorcycles for business purposes, reimbursement in respect of allowable motoring expenses can be effected by way of flat-rate mileage allowances.
There are two types of mileage allowance schemes which are acceptable for tax purposes if an employee bears all the motoring expenses:
- The prevailing schedule of Civil Service rates; or
- Any other schedule with rates not greater than the Civil Service rates
The Department of Public Expenditure and Reform has recently published circulars with new Civil Service Travel Rates, the revised rates are effective from 1st April 2017. The distance bands have increased from two to four with a lower recoupment rate for the first 1,500 kilometres.
Business travel carried out between 1st January and 31st March 2017 will not be affected by these new bands and rates, business travel to date from 1st January 2017 will count towards the cumulative business travel for the year.
Motor Travel Rates - Effective from 1st April 2017
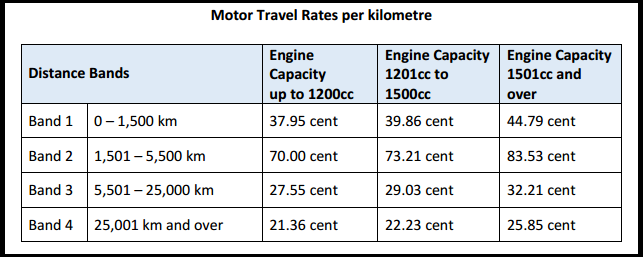
Reduced Motor Travel Rates per kilometre
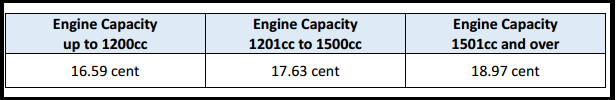
The reduced rates are payable to Civil Service employees who undertake a journey associated with their job but not solely related to the performance of their duties, such as:
- Attendance at confined promotion competitions
- Attendance at approved courses of education
- Attendance at courses or conferences
- Return visits home at weekends during a period of temporary transfer
The Motor Travel Rates for motorcycles and bicycles remain unchanged as follows:
Motorcycle:
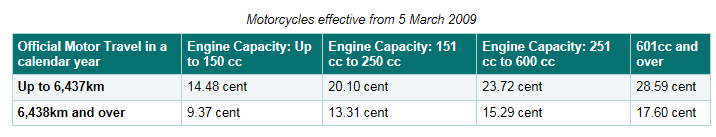
Bicycle: 8 cent per km
Please note, there are changes to subsistence rates which are also effective from 1st April 2017.
Please click here for the circular on Motor Travel Rates, and here for the circular on Subsistence
Mar 2017
20
New Illness, Maternity and Paternity Benefits rates in effect
Almost all welfare benefits and state pensions are to be increased in 2017.
The maximum weekly Illness Benefit payment will increase by €5.00 from €188 to €193 per week from week commencing 13 March 2017.
Illness benefit is considered as income for tax purposes and thus needs to be taken into account for PAYE purposes by an employer. It remains exempt from USC & PRSI.
No payment is made for the first six days of illness and for any Sunday.
Thesaurus Payroll Manager will automatically apply the increased rate of €193 per week as soon as Week 12 is reached in the software, which users should be aware of. Further information on how to process illness benefit in Payroll Manager can be found here:
In addition, standard Maternity and Paternity payments will increase from €230 to €235 per week from 13 March 2017. These are both taxable sources of income but aren’t liable to USC or PRSI. Unlike illness benefit, however, an employer must not tax these benefits through payroll. Instead, the Revenue will tax Maternity and Paternity Benefit via the employee’s tax credit Certificate by reducing the employee's SRCOP and tax credit on receipt of information from the Department of Social Protection.
Jan 2016
1
New Irish national minimum wage rate takes effect from 1 January 2016
The new hourly rate represents an increase of 50c on the previous figure and is the second increase to the minimum wage since 2011. Alongside the hourly pay increase, employer PRSI thresholds are being adjusted from 1 January to ensure that an increased PRSI burden does not fall on minimum wage employers.
- Experienced adult worker €9.15 per hour (was €8.65 )
- Over 19 and in 2nd year of first job €8.24 (was €7.79)
- Over 18 and in first year of first job €7.32 ( was €6.92)
- Aged under 18 €6.41 (was €6.06)
Minimum Wage for Trainees:
Employee aged over 18, in structured training during working hours
- 1st one third of course €6.86 (was €6.49 )
- 2nd third of course €7.32 (was €6.92 )
- 3rd part of course €8.24 (was €7.79)
Jun 2014
4
Changes to Holiday Pay Calculations
As we enter the summer holiday season employers need to ensure that they are paying their employees correctly during annual leave.
A recent decision by the European Court of Justice (ECJ) will impact how some annual leave pay is calculated.
Do you pay employee’s commission? Is the commission calculated based on the amount of sales made or actual work carried out? If yes, according to the ECJ, holiday pay should include commission pay.
The decision was made in the case of Locke v British Gas Trading and Others. Locke was a Sales Representative whose commission made up approximately 60% of his remuneration. After taking two weeks leave in 2011, Locke suffered financially as he was unable to generate sales for the period he was on annual leave.
The ECJ ruled that the purpose of annual leave is to allow a worker to enjoy a period of rest and relaxation with sufficient pay. By not including commission payments with holiday pay, employees are less likely to take annual leave so as to avoid financial hardship.
It has been left to the national courts to determine how to calculate the commission to which a worker is entitled, however the court did suggest that taking an average amount of commission earned over a certain period, e.g. the previous 12 months.
Employers are advised to review their commission policies to establish which, if any, payments need to be included in annual leave pay.










